Is Skin Pigmentation Permanent?
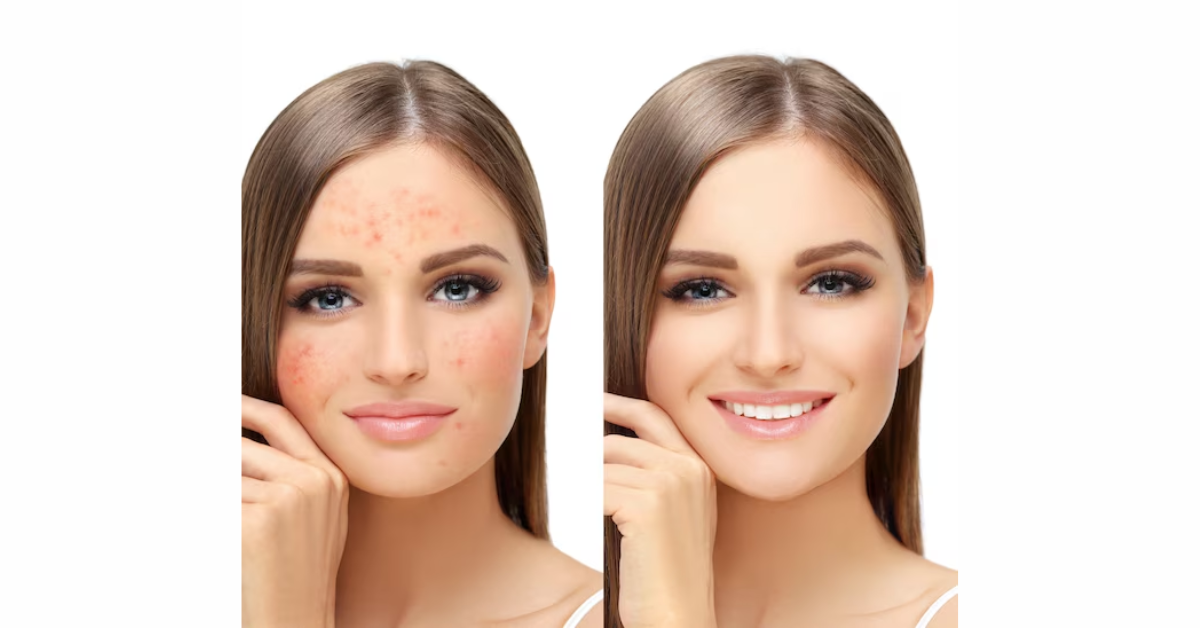
Skin pigmentation refers to the coloring of the skin, which is determined by melanin, a natural pigment produced by specialized cells called melanocytes. While pigmentation is normal and varies from person to person, certain conditions can cause uneven skin tone, dark patches, or discoloration. Many people wonder whether skin pigmentation is permanent or if it can be treated. The answer depends on the type of pigmentation, its causes, and the treatment options available. In this article, we will explore different types of skin pigmentation, what causes them, and whether they can be reversed.
Skin Pigmentation Explained
Pigmentation issues occur when the skin produces too much or too little melanin. This can result in hyperpigmentation (dark patches) or hypopigmentation (lighter patches). Several factors contribute to pigmentation changes, including sun exposure, hormonal fluctuations, genetics, and skin injuries.
Types of Skin Pigmentation and Their Permanency
1. Hyperpigmentation (Dark Spots and Patches)
Hyperpigmentation is the most common type of skin discoloration. It occurs when excess melanin is produced, leading to dark spots or patches on the skin. The most common forms include:
A. Melasma: Melasma appears as brown or grayish patches, mostly on the face. It is commonly triggered by hormonal changes, pregnancy, or birth control pills.
- Is it permanent? Melasma can fade over time with treatment, but it can also return with sun exposure or hormonal changes.
B. Sunspots (Liver Spots or Age Spots): These flat brown spots develop due to prolonged sun exposure, commonly appearing on the face, hands, and shoulders.
- Is it permanent? Sunspots can be treated with laser therapy, chemical peels, and topical treatments. However, without sun protection, new spots may appear.
C. Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH): PIH occurs after skin inflammation or injury, such as acne, burns, or cuts. The affected area darkens as part of the healing process.
- Is it permanent? PIH can fade naturally over time, but it may take months or years. Skincare treatments like vitamin C, retinoids, and exfoliation can speed up the process.
2. Hypopigmentation (Lighter Patches on the Skin)
Hypopigmentation occurs when the skin loses its natural color due to decreased melanin production. Common causes include:
A. Vitiligo: Vitiligo is an autoimmune condition where the body attacks melanocytes, leading to white patches on the skin.
- Is it permanent? Vitiligo is a lifelong condition, but treatments like phototherapy, corticosteroids, and skin grafts can help repigment the skin in some cases.
B. Albinism: Albinism is a genetic condition where the body produces little to no melanin, leading to pale skin, hair, and eyes.
- Is it permanent? Yes, albinism is permanent as it is caused by genetic factors. There is no cure, but individuals can protect their skin with sunscreen and avoid excessive sun exposure.
C. Post-Inflammatory Hypopigmentation: This condition occurs after an injury or skin condition, where the skin heals but lacks melanin in the affected area.
- Is it permanent? In many cases, the skin gradually regains color, but in severe cases, the discoloration may remain.
Treatment Options for Skin Pigmentation
While some pigmentation issues are permanent, many can be treated or improved with various treatments.
1. Topical Treatments
Certain creams and serums help lighten pigmentation over time.
- Hydroquinone – A skin-lightening agent that reduces melanin production.
- Vitamin C – An antioxidant that brightens skin and reduces dark spots.
- Retinoids – Help speed up cell turnover and fade pigmentation.
2. Chemical Peels
Chemical peels remove the top layer of skin to reveal fresher, more evenly toned skin underneath. They work well for sunspots, melasma, and PIH.
3. Laser Therapy
Lasers target melanin in dark spots, breaking it down to fade pigmentation. Different laser types are used depending on the severity of the pigmentation.
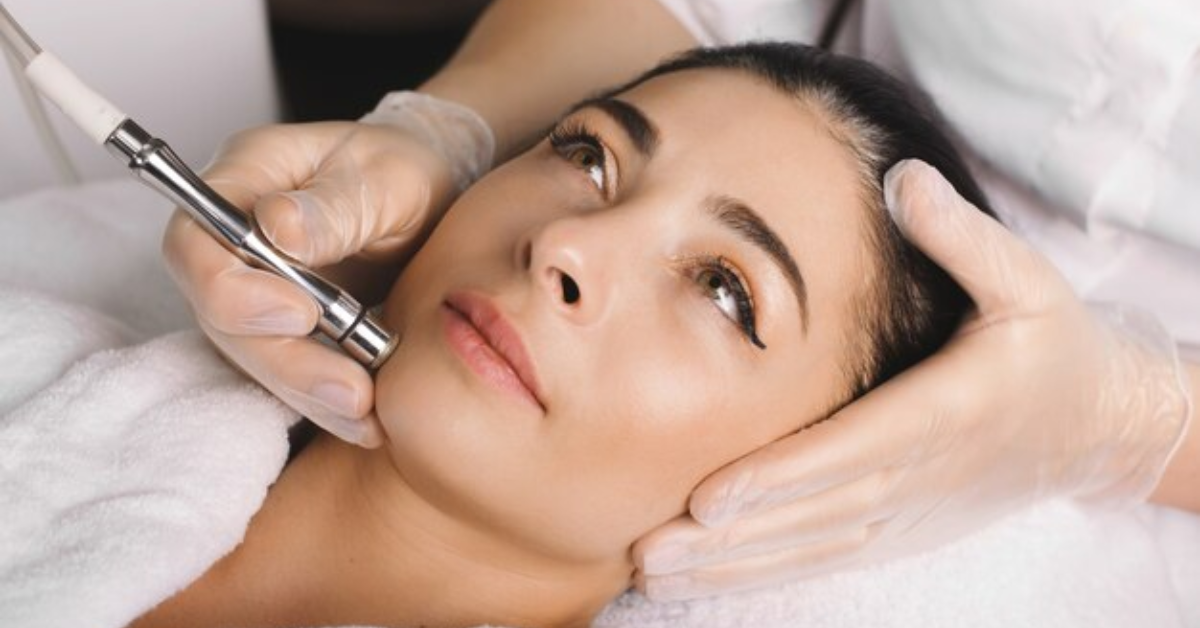
4. Microdermabrasion and Microneedling
These treatments exfoliate the skin and promote collagen production, helping to reduce pigmentation over time.
5. Sun Protection
Regardless of the type of pigmentation, sunscreen is crucial. UV rays trigger melanin production, worsening pigmentation issues. A broad-spectrum SPF of at least 30 should be applied daily.
Can Skin Pigmentation Be Prevented?
Although some pigmentation conditions are genetic or caused by uncontrollable factors, there are ways to minimize the risk:
- Wear sunscreen daily to prevent sunspots and melasma.
- Avoid picking at acne or wounds to prevent PIH.
- Use gentle skincare products to avoid irritation that can lead to pigmentation changes.
- Stay hydrated and maintain a healthy diet to promote overall skin health.
Final Thoughts
Is skin pigmentation permanent? The answer depends on the type and cause of pigmentation. While some conditions, like vitiligo and albinism, are permanent, others, such as sunspots, melasma, and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, can be treated or managed with the right skincare and professional treatments.
If you’re dealing with pigmentation concerns, consulting a dermatologist can help determine the best treatment plan for your skin type. With proper care and precautions, many forms of pigmentation can fade, allowing you to achieve a more even and radiant skin tone.