What Are the Common Signs of Skin Pigmentation?
Skin pigmentation refers to the coloring of the skin, primarily determined by melanin, a pigment produced by specialized cells called melanocytes. Abnormal skin pigmentation can manifest as discoloration, dark patches, or uneven skin tones due to factors like sun exposure, hormonal changes, genetics, or underlying medical conditions. Understanding the common symptoms can help you identify and address pigmentation concerns early.
The Pigmentation of Skin
The skin's pigmentation serves as a natural defense mechanism, shielding deeper layers of skin from harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays. However, disruptions in melanin production or distribution can lead to hyperpigmentation (darkened patches) or hypopigmentation (lightened areas). While pigmentation issues are usually harmless, they can impact self-esteem and may require medical evaluation to rule out serious conditions.
Common Symptoms of Skin Pigmentation Disorders
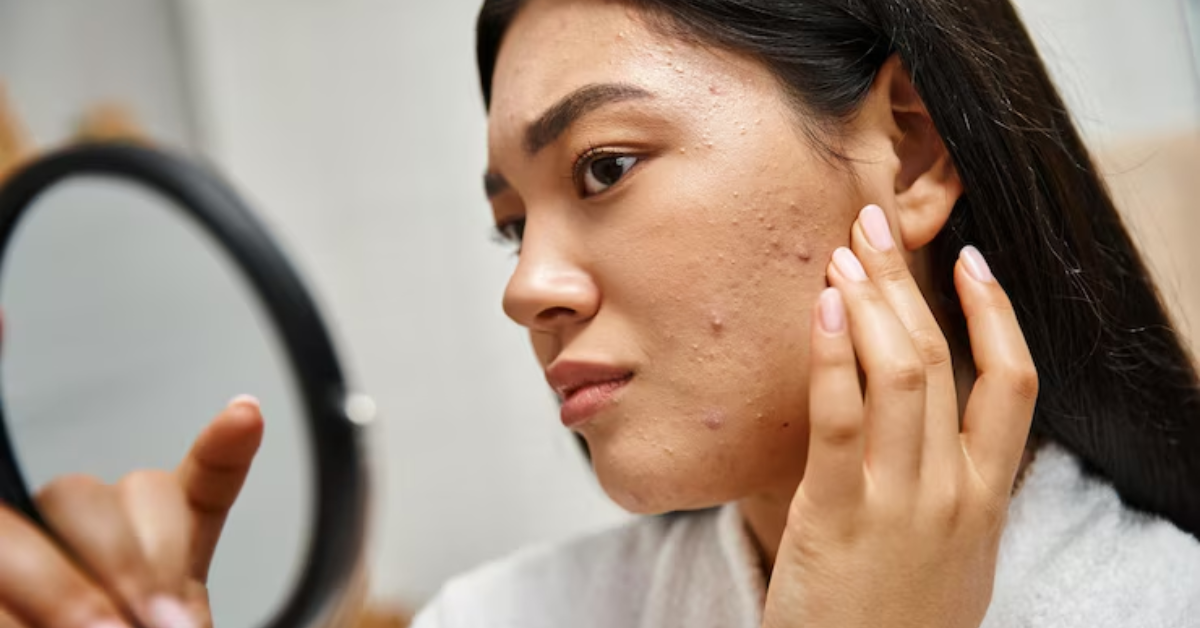
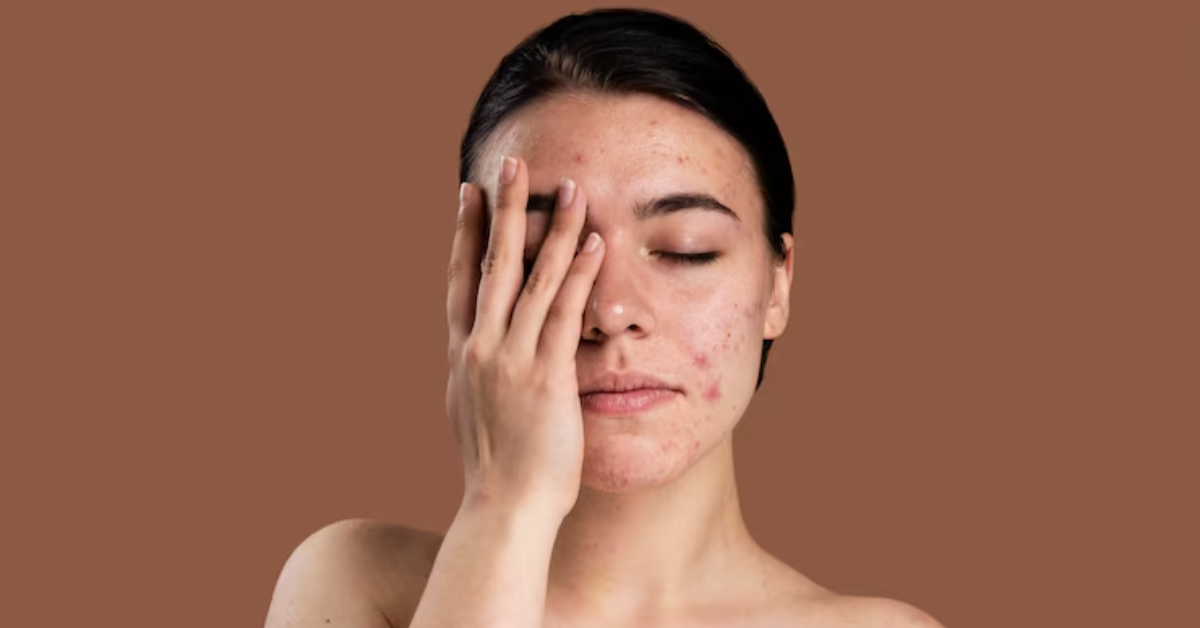
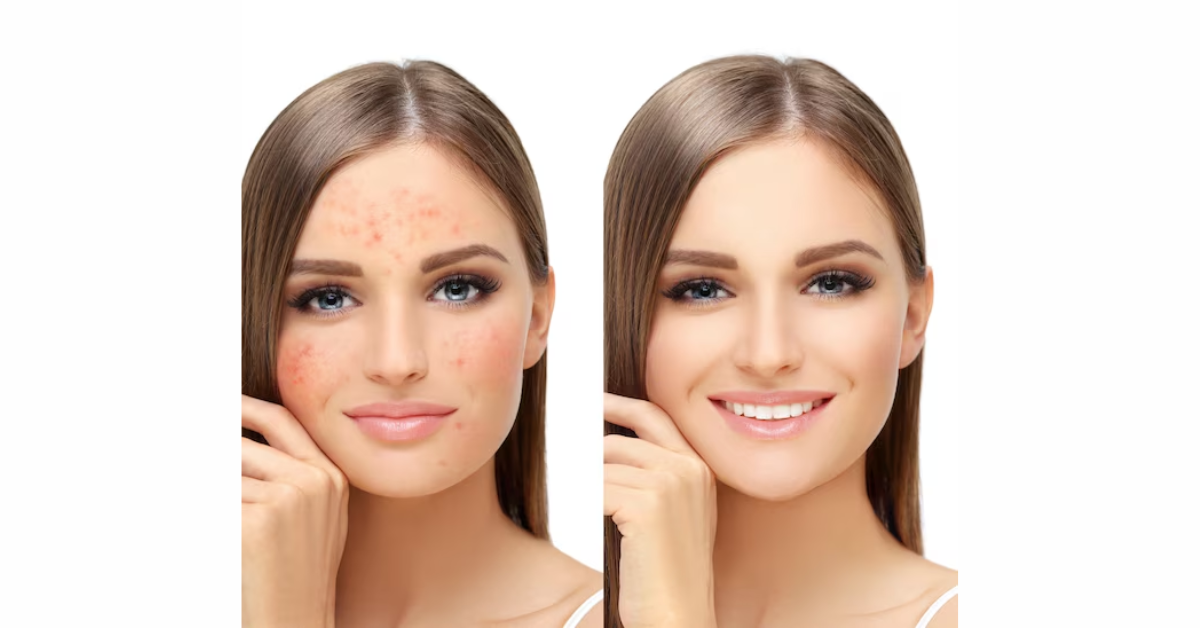
Dark Patches or Spots: Hyperpigmentation is a prevalent symptom where dark patches or spots appear on the skin. This occurs due to an overproduction of melanin, often triggered by:
- Sun Exposure: UV rays stimulate melanocytes, leading to sunspots or solar lentigines.
- Hormonal Changes: Melasma, common during pregnancy or hormonal therapy, causes large, dark patches on the face or other exposed areas.
Uneven Skin Tone: Discoloration or an inconsistent skin tone often signals pigmentation issues. Uneven tone can be subtle but noticeable, especially on the face, neck, or arms, where the skin is frequently exposed to sunlight.
Red, Pink, or White Patches: Hypopigmentation, characterized by the loss or reduction of melanin, manifests as lighter patches on the skin. Common conditions associated with hypopigmentation include:
- Vitiligo: A condition causing depigmented white patches.
- Post-Inflammatory Hypopigmentation: Occurs after skin trauma or inflammation, such as burns, acne, or eczema.
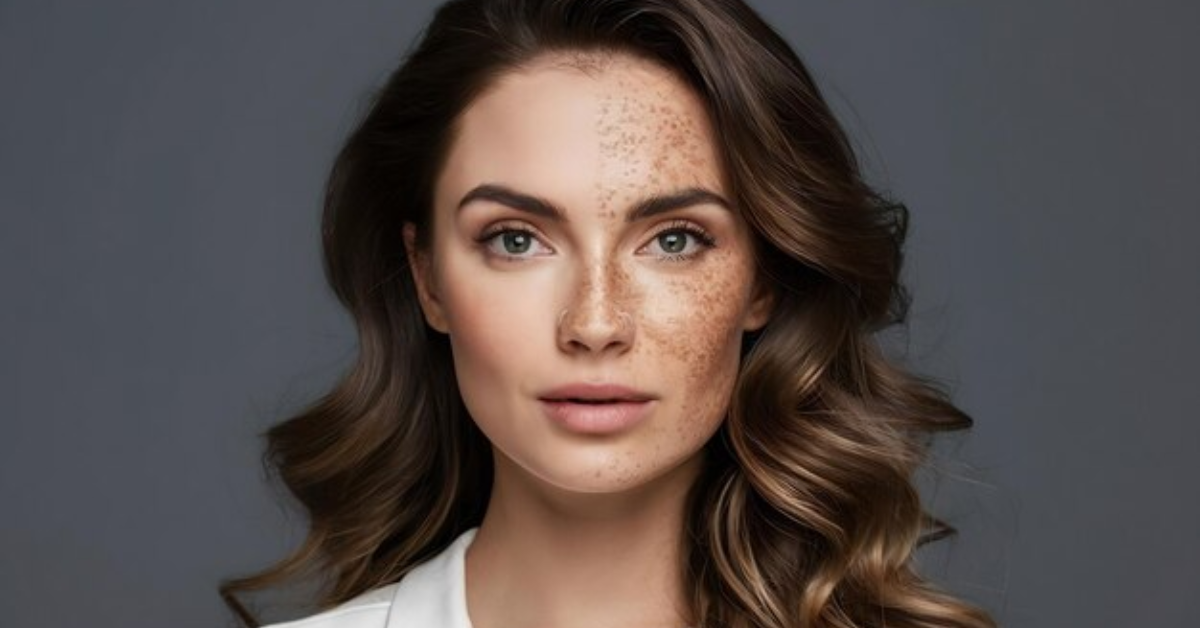
Freckles: Freckles are small, flat, brown spots often caused by genetic predisposition and sun exposure. They are harmless but can darken with continued UV exposure.
Age Spots: These flat, darkened areas appear on sun-exposed skin, particularly in older adults. While age spots are harmless, their appearance can mimic more severe conditions like melanoma, requiring a dermatologist’s evaluation.
Changes in Skin Texture: In some cases, pigmentation issues may coincide with changes in the skin's texture, such as roughness or thickened areas, particularly in chronic conditions like acanthosis nigricans.
Inflammation-Related Pigmentation: After injuries, burns, or infections, the affected areas may develop darker (post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation) or lighter (post-inflammatory hypopigmentation) spots, which may fade over time or persist without treatment.
Causes of Skin Pigmentation Symptoms
To better understand the symptoms, it’s important to recognize their causes. Common triggers include:
- Sun Exposure: Prolonged UV exposure leads to increased melanin production, causing dark spots or uneven tone.
- Hormonal Changes: Fluctuating hormones, particularly during pregnancy or menopause, can lead to conditions like melasma.
- Genetics: Conditions like freckles or albinism are genetically inherited pigmentation traits.
- Skin Trauma: Cuts, burns, or acne can result in pigmentation changes as the skin heals.
- Medical Conditions: Diseases like Addison’s disease, vitiligo, or thyroid disorders can affect pigmentation.
- Medications: Certain drugs, including chemotherapy agents and antibiotics, may cause pigmentation as a side effect.
Diagnosis and Treatment
If you notice any pigmentation symptoms, consult a dermatologist to determine the underlying cause. Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination and may include a Wood’s lamp test or skin biopsy.
Treatments vary depending on the severity and cause of the pigmentation. Common approaches include:
- Topical Treatments: Creams containing hydroquinone, retinoids, or vitamin C can lighten hyperpigmented areas.
- Chemical Peels: These remove the skin's outer layer, reducing pigmentation and promoting an even tone.
- Laser Therapy: Advanced laser treatments can target and break down excess melanin in specific areas.
- Sun Protection: Consistent use of sunscreen with a high SPF is essential to prevent further pigmentation.
Managing Skin Pigmentation Naturally
While medical treatments are effective, incorporating natural remedies and healthy habits can complement them:
- Sunscreen Application: Regularly use sunscreen to protect against UV damage.
- Hydration: Drinking water keeps the skin hydrated, aiding in the repair process.
- Balanced Diet: Foods rich in vitamins A, C, and E support healthy skin and melanin regulation.
When to Seek Medical Advice
Skin pigmentation is typically harmless, but some symptoms demand immediate attention. These include rapid changes in pigmentation, itching, bleeding, or pain in affected areas, and dark spots that increase in size, alter their shape, or develop irregular borders. Prompt evaluation by a dermatologist is crucial to ensure timely treatment and to rule out serious conditions such as skin cancer. For those seeking expert care and effective solutions, Malka Med Spa stands out as a trusted provider for skin pigmentation treatments, offering advanced therapies tailored to restore and enhance your skin's natural tone and health.
Conclusion
Skin pigmentation symptoms vary widely, from harmless freckles to noticeable patches of discoloration. While many pigmentation issues are cosmetic, they can indicate underlying health problems in some cases. By understanding the symptoms and causes, you can take steps to protect and maintain your skin’s health. Always consult a dermatologist for persistent or concerning pigmentation issues to ensure appropriate treatment and peace of mind.