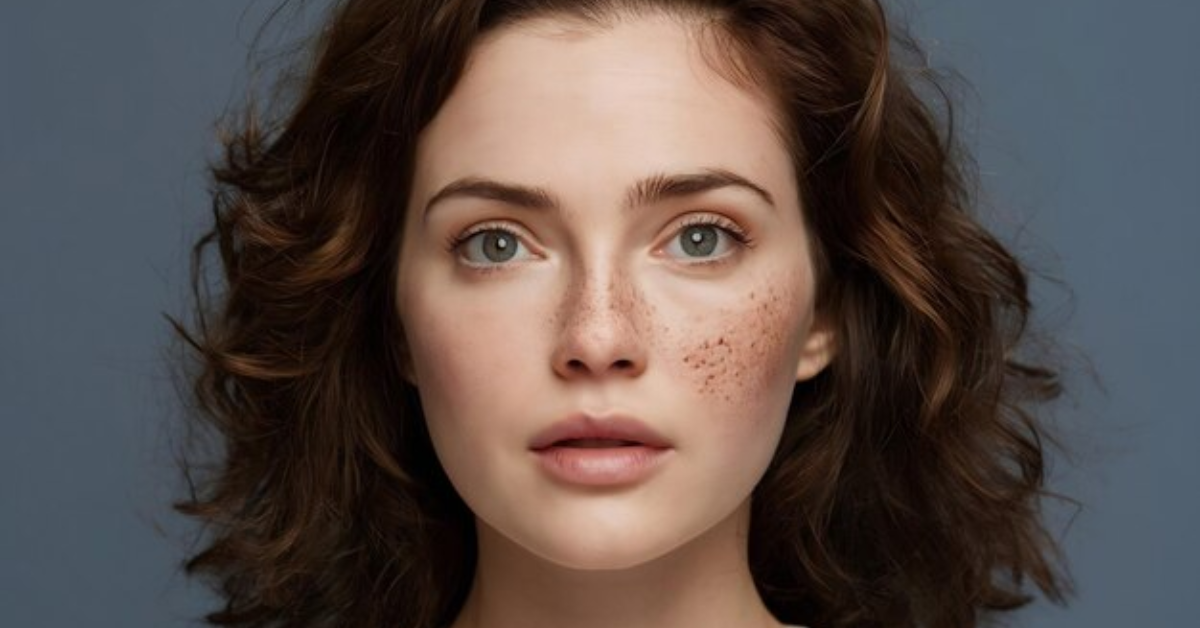
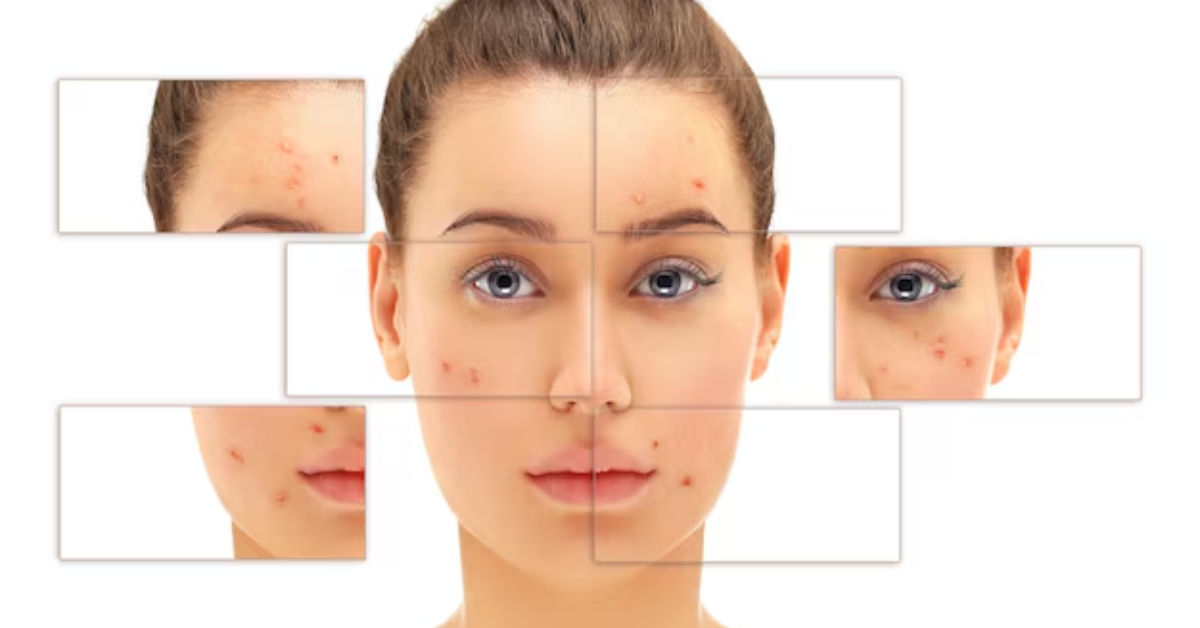
Pigmentation: What Makes It Worse and How to Stop It Early
Pigmentation is one of the most common skin concerns people struggle with—those stubborn dark spots, uneven skin tone, or patches that just won’t fade. For many, pigmentation begins subtly, but over time it can deepen due to daily habits, environmental triggers, or underlying skin conditions. Understanding what causes pigmentation and what makes it worse is the first step toward preventing it effectively. By taking early action and using the right skincare techniques, you can keep your skin bright, healthy, and even-toned.
In this guide, we’ll explore the root causes of pigmentation, the everyday factors that intensify it, and practical ways to stop it before it becomes harder to treat.
What Is Pigmentation?
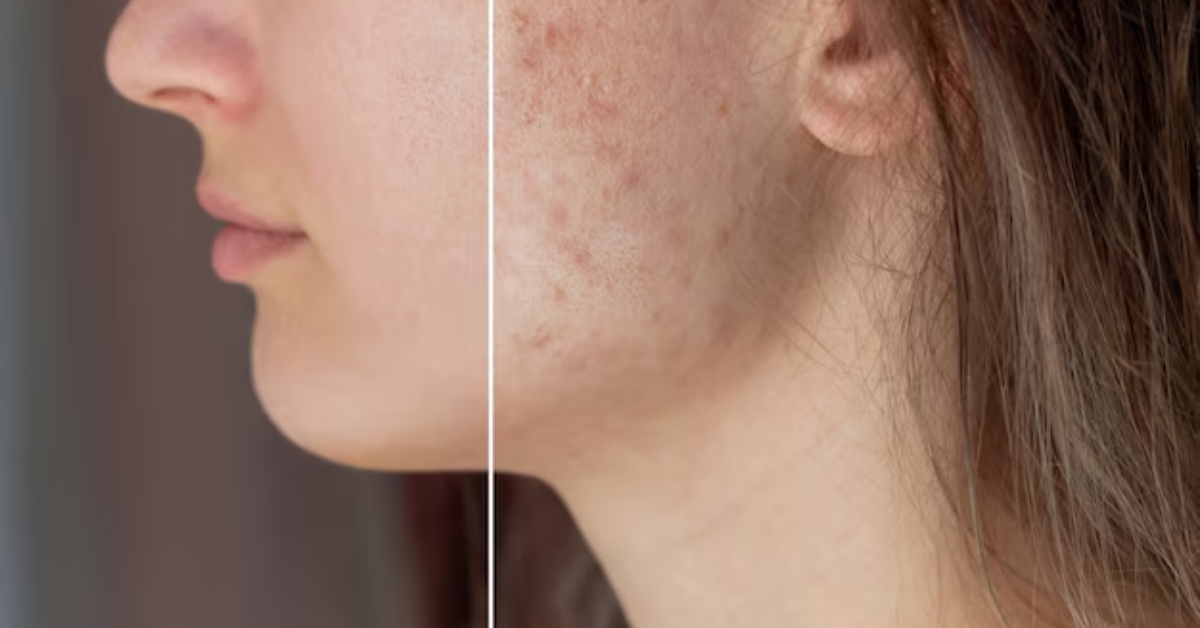
Pigmentation refers to the uneven darkening of the skin caused by excess melanin production. Melanin is the pigment that gives your skin, hair, and eyes their color. When the skin produces too much melanin in certain areas, dark spots or patches develop.
Common Types of Pigmentation
- Melasma – Often triggered by hormones, pregnancy, or sunlight.
- Sunspots / Age Spots – Caused by long-term sun exposure.
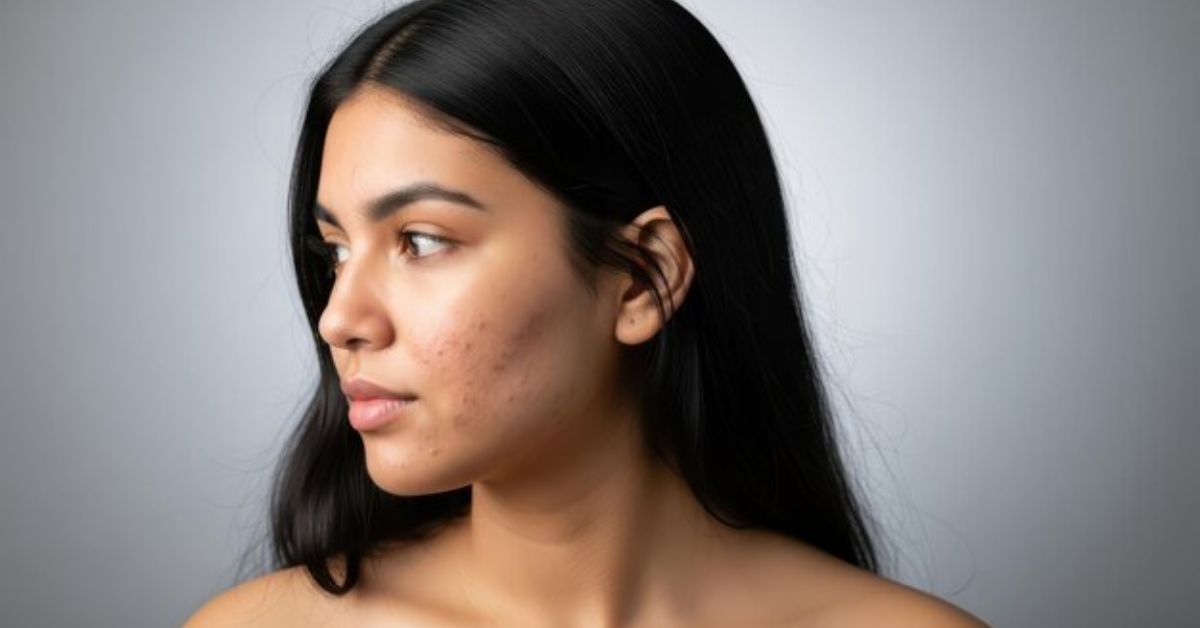
- Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH) – Marks left behind by acne, injury, or irritation.
Regardless of the type, pigmentation can worsen without proper care, which is why early prevention is crucial.
What Makes Pigmentation Worse?
Pigmentation is often triggered by more than one factor. Many everyday habits and conditions cause melanin to deepen or spread, making spots more visible. Here’s what commonly makes pigmentation worse:
1. Sun Exposure
Ultraviolet (UV) rays are the biggest culprit. Even a few minutes in the sun without protection can activate melanin production. Pigmentation may darken dramatically during summer or after spending time outdoors.
2. Heat Exposure
Even without direct sunlight, heat stimulates pigment cells. Activities like cooking, hot showers, saunas, and outdoor workouts can intensify pigmentation—especially melasma.
3. Hormonal Changes
Pregnancy, birth control pills, and hormonal imbalances can trigger melasma and make existing pigmentation more stubborn.
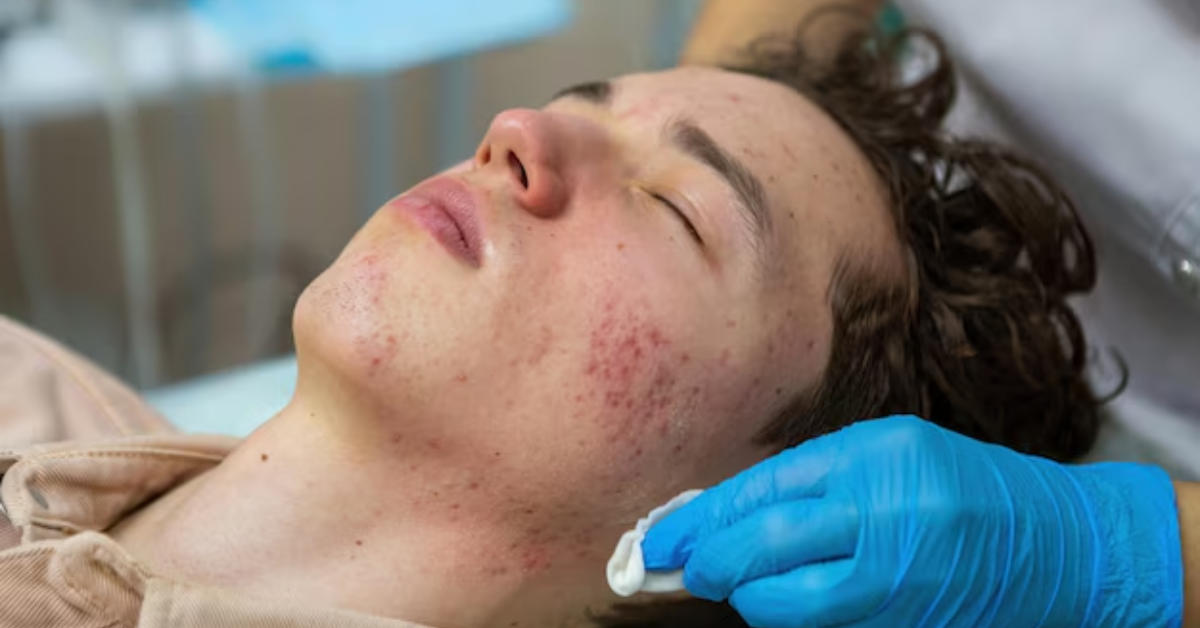
4. Skin Inflammation
Any skin injury—even tiny pimples—can leave dark marks. Picking at your skin, harsh exfoliation, or aggressive skincare routines often worsen PIH.
5. Incorrect Skincare Products
Using products that irritate the skin can lead to inflammation and, ultimately, darker pigmentation. Alcohol-heavy toners, strong fragrances, and bleaching creams often make things worse.
6. Genetics
Some people naturally produce more melanin. If pigmentation runs in your family, you may need to take preventive steps earlier.
7. Aging
As skin matures, its ability to repair UV damage slows down. This makes pigmentation more noticeable and harder to fade with age.
What Are the Common Symptoms of Skin Pigmentation?
How to Stop Pigmentation Early
The earlier you address pigmentation, the easier it is to control. With the right combination of sun protection, skincare ingredients, and lifestyle habits, you can significantly reduce the chances of it worsening.
1. Use Sunscreen Every Day
This is the most effective way to stop pigmentation from deepening. Choose a broad-spectrum SPF 30 or higher and reapply every two hours when outside.
Pro Tip: Look for sunscreens with zinc oxide or titanium dioxide—they protect against heat-induced pigmentation.
2. Add Brightening Ingredients to Your Routine
Skincare ingredients help fade existing pigmentation and prevent new spots.
Helpful ingredients include:
- Vitamin C – Brightens and reduces dark spots
- Niacinamide – Reduces inflammation and evens skin tone
- Azelaic Acid – Helps with PIH and melasma
- Alpha Arbutin – Lightens pigmentation effectively
- Retinol – Boosts cell turnover to fade marks
Use these consistently to see steady improvement.
3. Avoid Picking or Scratching Your Skin
Every time you squeeze a pimple or scratch irritation, you risk creating darker spots. A hands-off approach protects your skin barrier and reduces PIH.
4. Maintain a Gentle Skincare Routine
Look for products labeled non-comedogenic, fragrance-free, or for sensitive skin. Gentle care prevents inflammation, which is essential in controlling pigmentation.
5. Keep Your Skin Cool
If heat worsens your pigmentation:
- Avoid steaming hot showers
- Don’t place your face directly over stoves
- Use fans or cooling towels during workouts
Heat management makes a noticeable difference, especially with melasma.
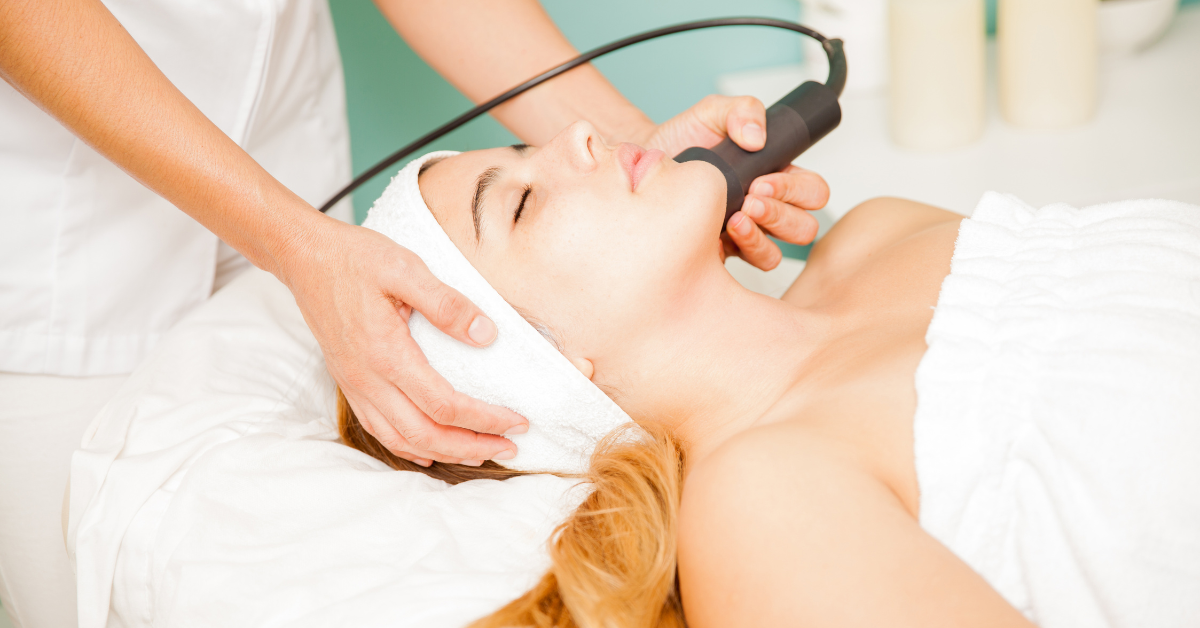
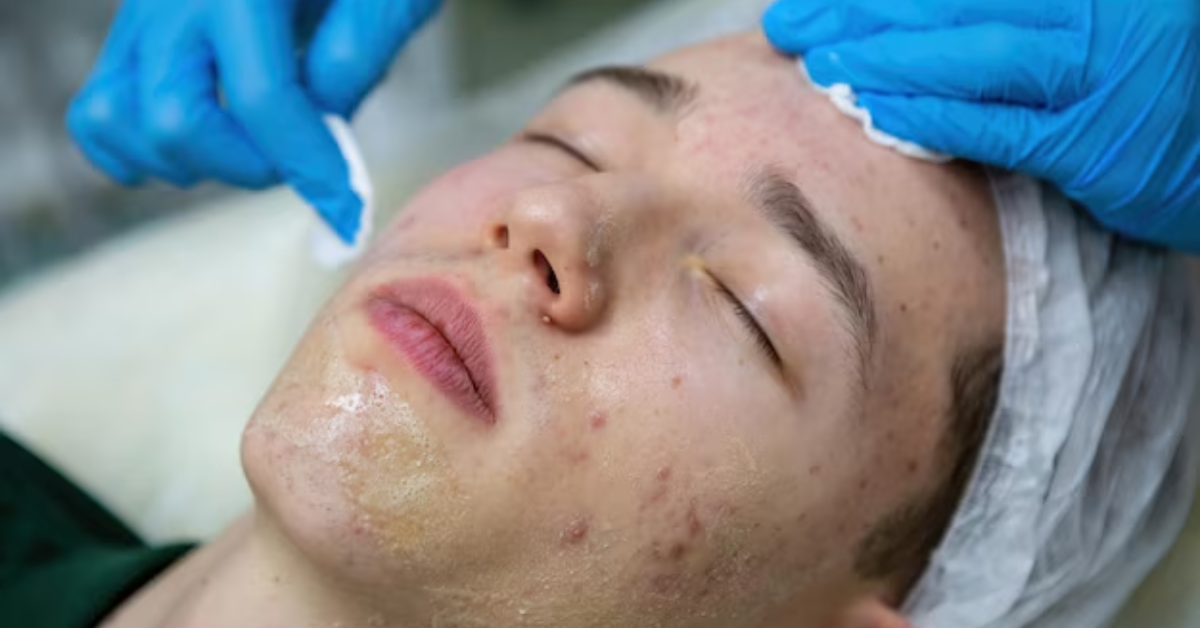
6. Try Professional Treatments
If pigmentation is severe, dermatologists may recommend treatments like:
- Chemical peels
- Laser therapy
- Microneedling
- Prescription creams (hydroquinone, tretinoin)
Always consult an expert to avoid worsening the pigmentation.
Can Pigmentation Be Fully Removed?
Some types—like light sunspots or acne marks—can fade completely. Others, like melasma, are chronic but can be significantly controlled with consistent care.
The key to success is early action, patience, and consistent use of sun protection and brightening products.
Conclusion
Pigmentation can be frustrating, but understanding its triggers helps you take control before it worsens. Sun exposure, heat, inflammation, and hormonal shifts are major contributors, but with the right preventive habits, you can stop pigmentation early and keep your skin clear and even-toned.
By protecting your skin, choosing the right skincare ingredients, and avoiding irritation, you give your complexion the best chance to stay bright and healthy. Consistency and gentle care are your strongest tools in preventing pigmentation from becoming a long-term concern.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What is the fastest way to reduce pigmentation?
A: Using sunscreen daily and applying brightening ingredients like vitamin C and alpha arbutin helps fade pigmentation quickly.
Q2. Can pigmentation go away naturally?
A: Mild acne marks or sunspots may fade over time, but most pigmentation needs skincare treatment and sun protection to fade completely.
Q3. Does heat really worsen pigmentation?
A: Yes. Heat activates pigment cells, especially in people with melasma. Managing heat exposure is essential.
Q4. Can I treat pigmentation during pregnancy?
A: Stick to safe ingredients like niacinamide, azelaic acid, and vitamin C. Avoid retinol unless approved by your doctor.
Q5. What foods help reduce pigmentation?
A: Foods rich in antioxidants—berries, leafy greens, citrus fruits—help support skin repair and brightness.