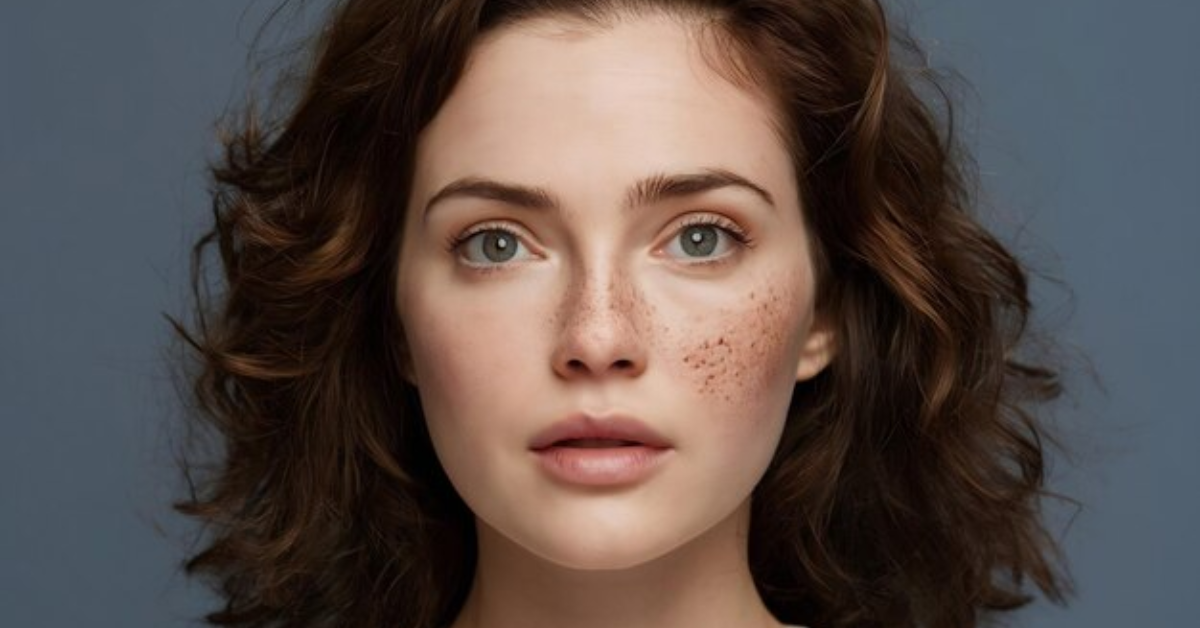
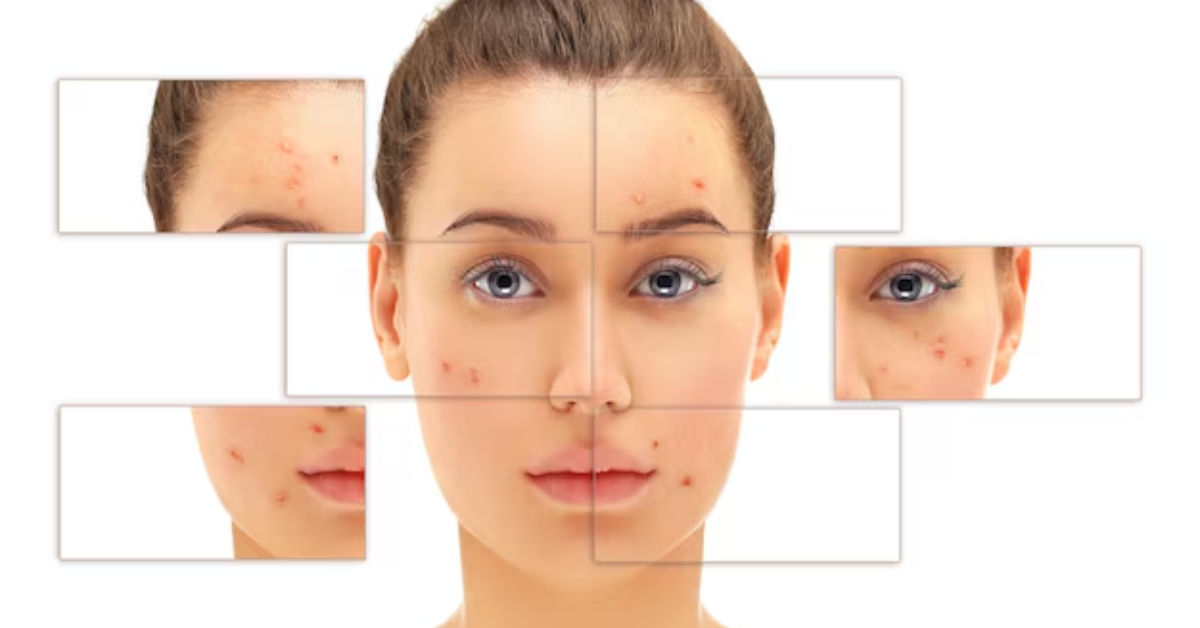
Everything You Wanted to Know About Skin Pigmentation
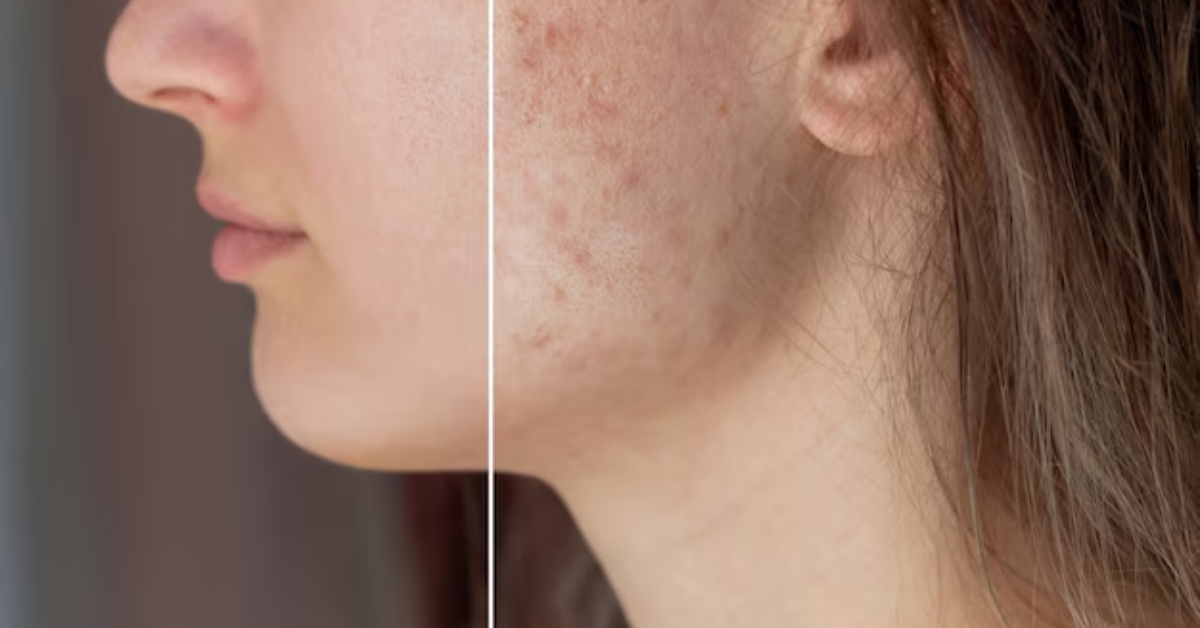
Skin pigmentation is one of the most common concerns people experience, regardless of age or skin type. From dark spots and melasma to post-acne marks and tanning, pigmentation issues can affect confidence and make skincare feel overwhelming. The good news? Understanding skin pigmentation—why it happens, what triggers it, and how to manage it—can help you choose the right treatments and care routine. This guide breaks everything down in a simple, human way so you know exactly what your skin needs.
What Is Skin Pigmentation?
Skin pigmentation refers to the natural coloring of your skin, determined by a pigment called melanin. Melanin is produced by cells known as melanocytes, and the amount of melanin your body makes defines whether your skin is light, medium, or dark.
However, when melanin production becomes unbalanced—either too high or too low—you may develop pigmentation problems. This imbalance can be temporary or long-term, depending on the cause.
Types of Pigmentation Issues
Not all pigmentation looks the same, and knowing the difference helps you find the right treatment.
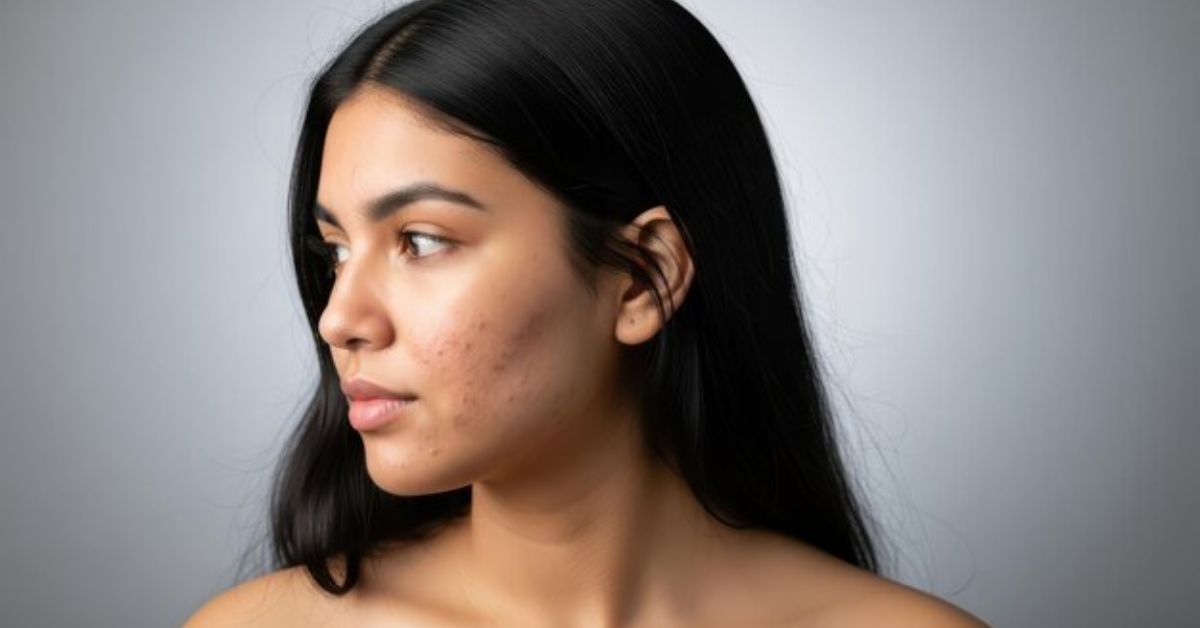
1. Hyperpigmentation
This is the most common type and happens when excess melanin forms dark patches or spots. It usually appears as:
- Sunspots or age spots
- Melasma
- Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) from acne or injuries
Hyperpigmentation is not dangerous, but it can be cosmetically frustrating.
2. Hypopigmentation
When melanin production drops, the skin becomes lighter than the surrounding areas. Common causes include eczema, infections, or healing wounds.
3. Melasma
Melasma looks like large, patchy brown areas—usually on the cheeks, forehead, and upper lip. It is often triggered by:
- Hormonal changes
- Pregnancy
- Sun exposure
- Birth control pills
Melasma can be stubborn and requires consistent management.
Common Causes of Skin Pigmentation
Pigmentation issues rarely appear without a trigger. Understanding these triggers can help you reduce or prevent spots in the future.
Sun Exposure: UV rays are the number one cause of uneven skin tone. When your skin is repeatedly exposed to the sun, it produces more melanin as a defense mechanism, leading to tanning and dark spots.
Hormonal Changes: Pregnancy, menopause, and hormonal medications can increase melanin production. That’s why melasma is often called “the mask of pregnancy.”
Acne and Inflammation: Any injury—like acne, burns, cuts, or eczema—can leave dark marks behind. This is known as post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
Genetics: If pigmentation issues run in your family, you may be genetically inclined to develop them.
Medications:Certain drugs, including antibiotics and chemotherapy medicines, can cause pigmentation changes.
Aging: As we age, melanin distribution becomes uneven, leading to age spots and dullness.
How to Treat Skin Pigmentation Effectively
There’s no one-size-fits-all solution, but combining skincare and professional treatments often gives the best results.
Top Skincare Ingredients for Pigmentation Treatment
- Vitamin C: A powerful antioxidant that brightens the skin and fades dark spots by reducing melanin production. It’s gentle and suitable for most skin types.
- Niacinamide: Helps with brightening, calming inflammation, and evening out skin tone. Great for sensitive skin.
- Retinoids (Retinol): Encourage skin renewal and reduce the appearance of stubborn pigmentation. Best used at night.
- Alpha Hydroxy Acids (AHAs): Ingredients such as glycolic acid exfoliate dead skin cells, revealing a brighter layer underneath.
- Azelaic Acid: Ideal for acne-prone or sensitive skin, as it helps fade pigmentation while reducing inflammation.
- Kojic Acid: A natural lightening ingredient that effectively targets melanin production.
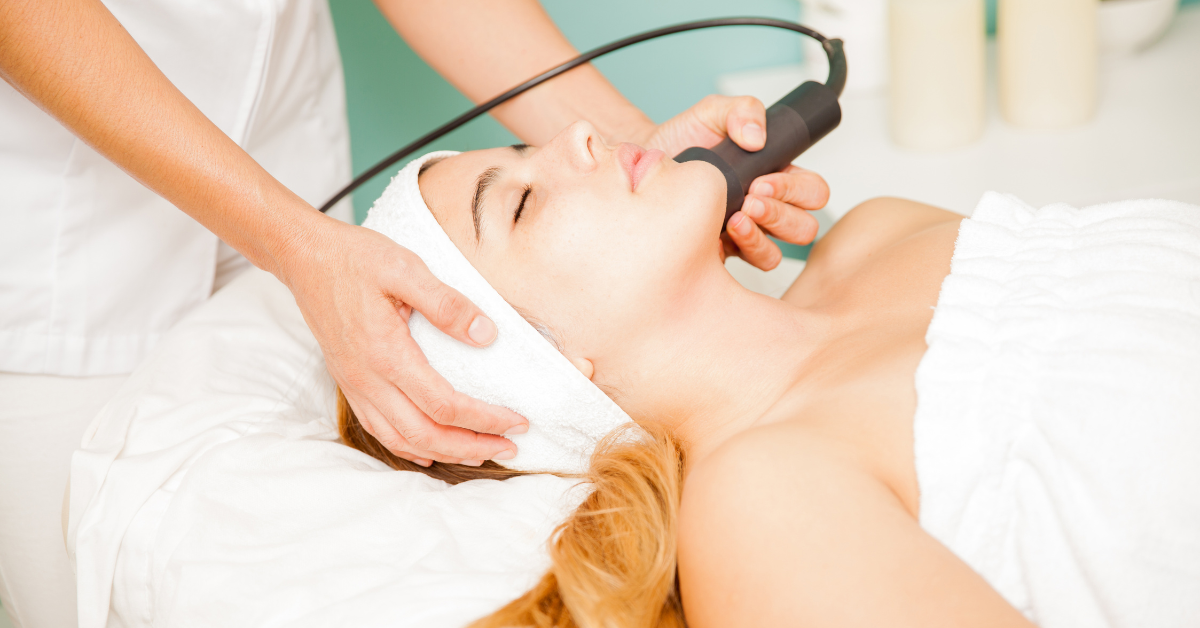
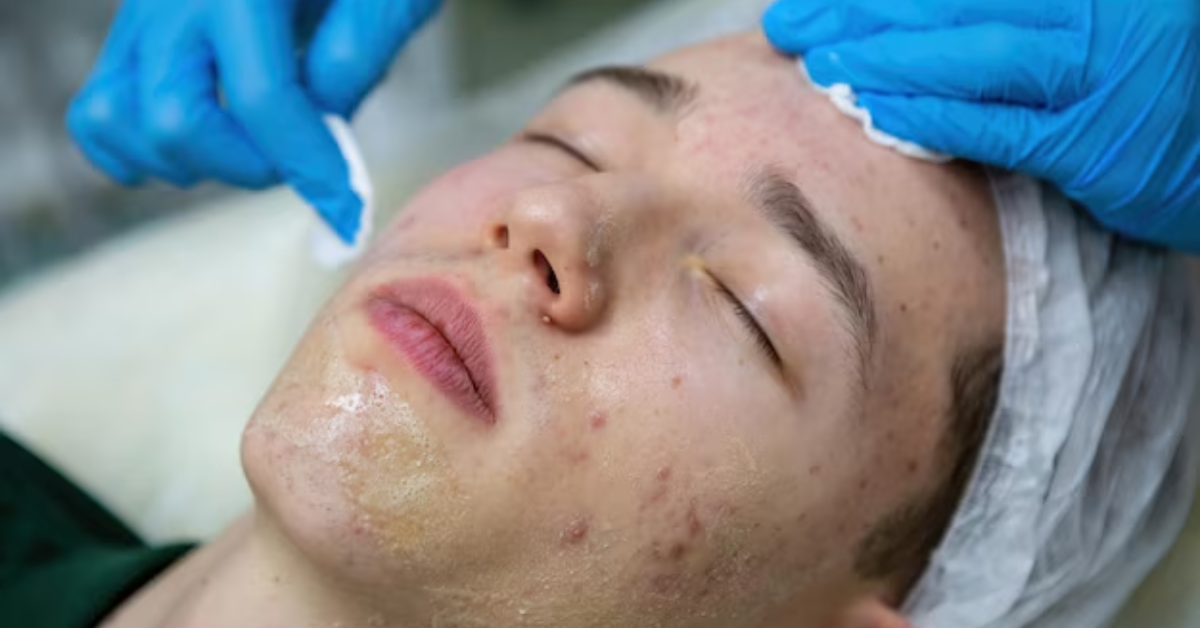
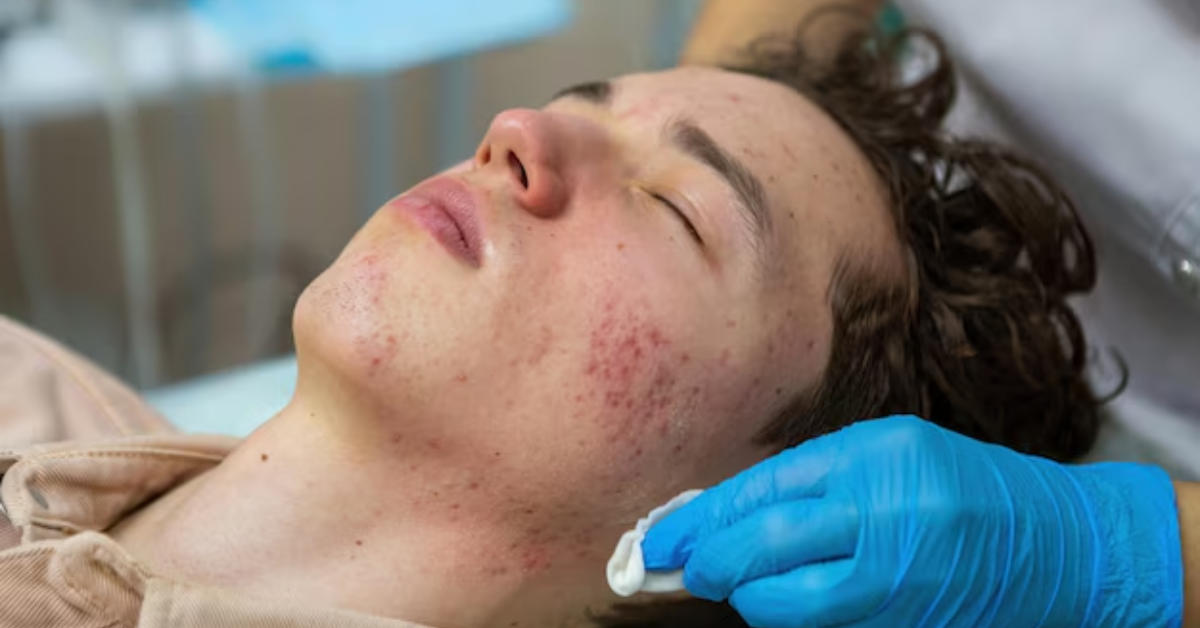
Professional Pigmentation Treatments
If skincare products aren’t giving you the results you want, dermatologists offer advanced treatments:
- Chemical Peels: These remove the top layer of skin, reducing dark spots and improving texture.
- Laser Therapy: Targeted lasers break down excess melanin and boost collagen. Different lasers are used depending on your skin tone.
- Microneedling: Creates tiny micro-injuries that stimulate healing and allow pigmentation products to work better.
- Hydrafacial With Brightening Boosters: Deeply cleanses and exfoliates while infusing brightening serums for instant glow.
Always consult a professional, especially if you have darker skin, as some treatments carry risk of worsening pigmentation.
How to Prevent Pigmentation From Getting Worse
Treating pigmentation is only half the journey—you also need to prevent new spots from forming.
- Use Sunscreen Daily: Nothing matters more than SPF. Choose a broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 50 and reapply every two hours if you’re outdoors.
- Avoid Picking Pimples: Picking increases inflammation, which leads to darker acne marks.
- Stick to a Consistent Routine: Pigmentation takes time to fade. Consistency is key—results are usually visible in 8–12 weeks.
- Wear Hats or Seek Shade: Extra protection goes a long way, especially for melasma.
When to See a Dermatologist
If your pigmentation is spreading, very dark, or not improving after 2–3 months of treatment, it’s best to seek professional help. Sudden pigmentation changes can sometimes be linked to medical conditions.
Conclusion
Skin pigmentation can be frustrating, but with the right knowledge, it becomes much easier to manage. Understanding your skin, choosing effective ingredients, and protecting yourself from sun exposure are the cornerstones of an even, glowing complexion. Whether you deal with hyperpigmentation, melasma, or post-acne marks, remember—consistency and patience lead to real results.
FAQs About Skin Pigmentation
Q1. What is the fastest way to remove pigmentation?
A: Professional treatments like chemical peels and lasers work quickly, but consistency with brightening skincare also helps.
Q2. Can pigmentation go away naturally?
A: Some types, like post-acne marks, fade on their own. Others, like melasma, need long-term treatment.
Q3. Does sunscreen prevent pigmentation?
A: Yes! Sunscreen is the number one way to stop pigmentation from worsening or coming back.
Q4. Which skincare ingredient is best for pigmentation?
A: Vitamin C, niacinamide, kojic acid, and retinoids are among the most effective ingredients.
Q5. Are home remedies safe for pigmentation?
A: Some may cause irritation or worsen dark spots. Dermatologist-approved products are safer and more effective.